Fungal infections are regarded as a serious health threat worldwide because they cause severe mucosal and systemic candidiasis in elderly people and patients with AIDS, organ transplantation or immunodeficiency. C-type lectin receptors (CLRs) dectin-1, dectin-2/3 and Mincle play a pivotal role in recognizing fungal cell wall components and activating protein kinase Syk, thereby initiating anti-fungal innate and adaptive immune responses. Whereas the TH1 cells have been linked to fungal infection, the TH17 cells are the main T cell subset responsible for eliminating fungal pathogens. Therefore, better understanding of the mechanisms by which CLRs activate Syk and Syk-dependent TH17 responses may lead to the development of new strategies to combat fungal infections.
A research group led by Prof. XIAO Hui from the Institut Pasteur of Shanghai, CAS identified a crucial role for the tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 in mediating CLR-induced activation of Syk. Ablation of the gene encoding SHP-2 in dendritic cells (DCs) and macrophages impaired Syk-mediated signaling and abrogated the expression of genes encoding pro-inflammatory molecules following fungal stimulation.
Their study shows SHP-2 operated as a scaffold, facilitating the recruitment of Syk to the CLR dectin-1 or dectin-2/3-FcRg through a previously unrecognized ITAM motif. In addition, SHP-2-mediated CLR signals in DCs play an indispensable role in the induction of anti-fungal TH17 responses in vivo.
A paper about this work entitled “Tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 mediates C-type lectin receptor–induced activation of the kinase Syk and anti-fungal TH17 responses” was online published in Nature Immunology on April 27th, 2015.
This work is supported by the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Ministry of Science and Technology and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
AUTHOR CONTACT:
Dr. XIAO Hui
Unit of Immune Regulation and Signaling, Institut Pasteur of Shanghai, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China 200031
E-mail: huixiao@ips.ac.cn
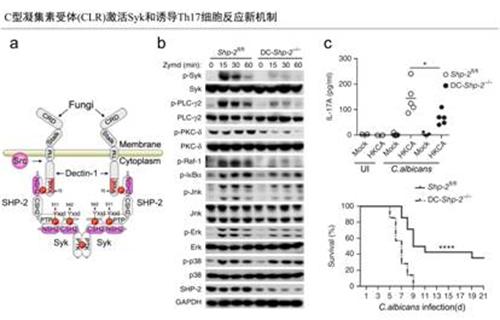
Fig a A schematic presentation of SHP-2 acting as an adaptor to recruit Syk to dectin-1.
Fig b SHP-2 plays a pivotal role in the activation of Syk and its down stream signaling molecules in dectin-1 pathway.
Fig c SHP-2 DC-deficient mice failed to produce effective Th17 responses to control fungal infection.
link:http://www.nature.com/ni/journal/vaop/ncurrent/full/ni.3155.html

