Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) is a mosquito-borne flavivirus. The infectious disease it causes is encephalitis. China is one of the countries with high incidence of encephalitis. Only a limited number of JEV-infected individuals show symptoms and induce severe encephalitis, that indicating host-dependent susceptibilities. Clinical disease varies from nonspecific febrile illness to encephalitis, even to death in about one of every 250 infected individuals. The reason that people have different susceptibilities to JEV remains unclear. Low viremia detected in patients leads to the difficulty of early diagnosis of JEV infection.
Clinical manifestations of JEV infections in laboratory mice closely resemble human symptoms. Therefore, mice have been used to study JEV infection. Miss Kai Wang, Ph.D.student at the Institut Pasteur of Shanghai, Chinese Academy of Sciences, surpervised by Prof. Vincent Deubel, revealedthat the comparative in vivo mouse infection did not show clear-cut differences in viral or soluble markers of innate immunity among highly susceptible and less susceptible mouse strains. However, earlier and greater amounts of neutralizing antibodies could have limited the invasion of JEV in the brain in less susceptible mice. Moreover, a lower JEV infectivity capacity was observed in bone marrow-derived primary macrophages and dendritic cells of the less susceptible mouse strain. These differences represent biological factors which may contribute to partial protection against JEV neuroinvasion in less susceptible mouse strains.
This study was supported by Shanghai Pasteur Health Research Foundation and was published in PLos One. 2011;6(9):e24744.Epub 2011 Sep 16.
Mice with Different Susceptibility to Japanese Encephalitis Virus Infection Show Selective Neutralizing Antibody Response and Myeloid Cell Infectivity
Kai Wang, Vincent Deubel¤*
Key Laboratory of Molecular Virology and Immunology, Institut Pasteur of Shanghai, Shanghai Institute for Biological Sciences, Shanghai, China
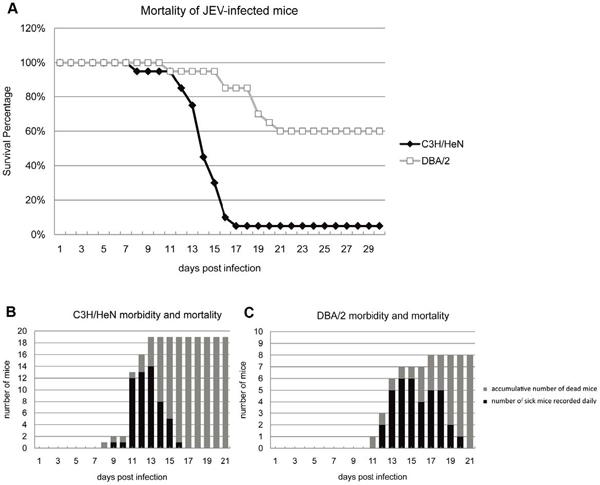
Mortality of C3H/HeN and DBA/2 mice after intraperitoneal infection with JEV.

