On April 22, a study from the Key Laboratory of Molecular Virology and Immunology at the Institut Pasteur of Shanghai, Chinese Academy of Sciences(IPS-CAS) was released in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, entitled “TIP60 Positively regulates ThPOK-Mediated Repression of Eomesodermin in Human CD4+ T Cells”. This study reveals the role of ThPOK in the repression of Eomes expression by binding to its promoter in human CD4+ T cells. As Eomes is required for the expression of IFNγ, this study has revealed a novel pathway in which type I proinflammatory cytokines are controlled in immune cells.
In this paper, LI Yangyang, a third-year MS/Ph.D student in Dr. LI Bin’s research group has found that short-term TCR stimulation promotes the lysine acetyltransferase TIP60 association with and acetylation of ThPOK to prevent its degradation. Furthermore, TIP60 was found to stabilize ThPOK by acetylation of its K360 residue to potentiate the transcriptional repression of Eomes. This new role of TIP60 adds to those previously described by the team in terms of immune regulation. These previous studies have shown how TIP60 regulates regulatory T cells through binding to the FOXP3 transcriptional complex to direct anti-inflammatory programs in these cells.
Further understanding of how TIP60 functions in Treg cells and other immune cells could provide therapeutic targets for restricting anti-inflammatory responses to allow for the trigger of pro-inflammatory pathways to tackle infection and cancer.
The research project is supported by the NSFC grants, Shanghai ‘Rising Star’ program and Knowledge Innovation Program of Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, CAS.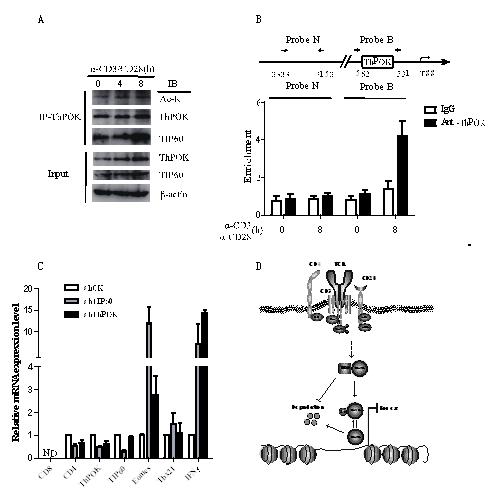
Figure. TIP60 positively regulates ThPOK-mediated repression of Eomes. A, Short-term TCR stimulation stabilizes ThPOK by promoting TIP60 association with and acetylation of ThPOK. B, ThPOK binds to the promoter region of Eomes upon TCR stimulation. C, The depletion of TIP60 or ThPOK in CD4+ T cells resulted in the increasing expression of Eomes and IFNγ. D, Working model describing the role of TIP60 for ThPOK-mediated repression of Eomes.

